And by definition the atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in it. So the atomic number of a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons or the number of electrons in the atom. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Explanation: For an atom to be neutral, all the charges have to equal zero. Because protons are charged +1 and electrons are charged -1, the number of protons has to be equal to the number of electrons for the charges to cancel out. For a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Atoms and Atomic Structure Chemistry Elements and Compounds Physics Relationships Genetics Periodic Table Science.
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons. *
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
- In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Neutrons
How do you calculate the number of protons in a neutral atom?
1 Answer
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
The neutral atom will have the same number of protons as the number of electrons in the ground state.
Explanation:
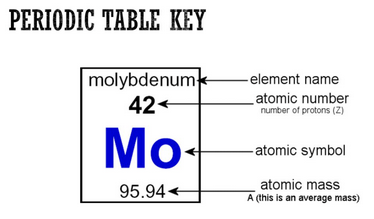
To be “neutral” and atom must have the same number of protons as electrons. Usually it is the electrons that are shared, acquired or lost in chemical bonding.
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons. *
The “ground state” of an atom will have a fixed number of electrons that define its chemical properties. The number of electrons can be determined from an atom’s position in the Periodic Table – or simply looked up in that table or other reference.

In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons
The neutral atom will have the same number of protons as the number of electrons in the ground state.
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Neutrons
Related questions
